|
|
.jpg)
by Makya Rodriguez, age 17
The mighty bald eagle is facing some tough times. In recent years, the population of our national bird has decreased by almost 4%, and lead poisoning is usually the reason.
A new nationwide study has found that up to 33% of examined dead bald eagles contained serious levels of lead poisoning. This clinical poisoning is mainly transmitted from an eagle’s prey such as fish or small animals. After consuming such prey, the eagles’ stomach acids break down neurotoxin and release lead into the bird’s bloodstream. The lead then travels to soft tissues around the body and eventually accumulates within the bird’s bones leading to the death of these beautiful animals.
In colder seasons eagles tend to go from natural hunters to scavengers. Scientists have found that eagles are more likely to get poisoned during the colder months when they depend more on the tainted remains of dead prey.
[read more]

by Dayanara Flores Gonzalez, age 14
The Sugar River, also known as The Upper Sugar River Watershed, is located in Dane County and flows all the way down to the Rock River.
The Upper Sugar River Watershed Association works to protect the river from invasive species that can harm or push out native species and damage the ecosystem. Many rare and endangered native plants found in the river and its nearby wetlands are threatened. Most wetland animals depend on these native plants for food and shelter.
Some native species can disappear if a watershed loses its healthy wetlands. Recreational uses of wetlands include trapping, fishing, bird watching, and nature study. Healthy wetlands can help with keeping the water clean and safe for wildlife. Healthy wetlands also help control and prevent floods.
[read more]

by Sarah Thomson, age 13
Imagine a future where storms, droughts, and floods are much more destructive and much more common than they are today. In this foreseeable future, the world's ecosystems have altered significantly with polar bears and many other animals extinct and others migrating across the globe. Diseases exist in areas they had never been before. Many experts believe this future could become a reality if humans do not slow down the current global warming problem.
Global warming is caused by humans burning fossil fuels like coal and oil. Burning these fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide and other gases – known as “greenhouse gases” – trap some of the sun's heat in Earth's atmosphere. This process is called the “greenhouse effect” because it acts as a greenhouse in the manner in which it retains heat. This is what keeps Earth at a livable temperature. However, as more greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, more heat is trapped, warming the Earth more than what naturally occurs. As humans burn fossil fuels to meet their energy demands, the Earth faces serious problems.
Global warming causes huge amounts of climate change around the globe. Glaciers and ice sheets are melting at the poles, raising sea levels. This is creating problems for coastal settlements. Natural disasters like floods, droughts, and hurricanes will become more common and more severe. The changes in climate will also affect animals and ecosystems. Some animal species may become extinct while others move across the globe to new areas where they can survive. This migration could cause the spread of diseases. For instance, mosquitoes will be able to carry diseases such as malaria and the Zika virus to many more areas. Global warming isn't a simple matter of a slightly warmer planet: it is causing a series of serious problems that will only get worse unless people do something about it.
[read more]

by Sanaai Brazil-Broach , age 12
Are genetically modified foods safe to consume?
Over the last two decades, food that consumers have eaten contains genes from other plants that make them either grow faster, taste better or stay fresher for a longer period of time. Foods that have been altered this way are called “genetically modified foods.”
Some reasons companies may modify food is because they want it to look more appealing, or they are trying to give people the vitamins that their bodies need. Each year, for example, around half of a million children go blind, and one or two million children die from the lack of vitamin A. So scientists have developed vitamin A in rice and put it in other foods to help solve this problem.
[read more]

by Abigail Comerford, age 14
The lesser long-nosed bat is no longer endangered thanks to conservation made possible by scientists and volunteers. It is the first U.S. bat to escape endangerment. The bats' recovery is thanks to cooperation between the United States and Mexico.
Amy Lueders, the southwest regional director for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, claims that science shows that threats to the species have decreased to the point of the bats' recovery.
She also states, “the Service is proud of our strong, decades-long partnership with very diverse stakeholders on behalf of the lesser long-nosed bat. Without partnerships and collaborations such as these, successful recovery would not be possible.”
[read more]
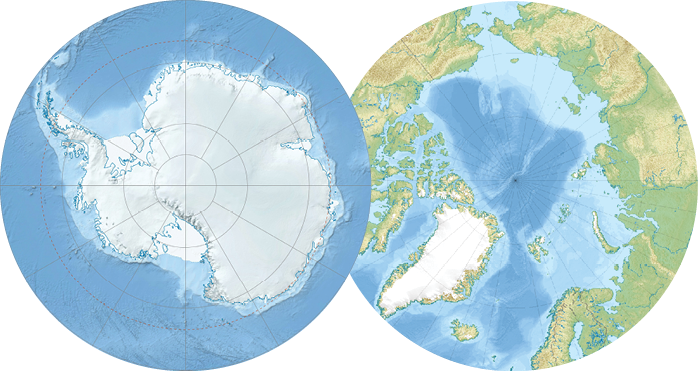
by Felix Berkelman, age 14
Although one might think the Arctic and Antarctic seem basically the same climate wise, they are actually noticeably different. Likewise, they are also affected differently by climate change. Both areas have melting ice, however the two poles have it for a different reason.
The main reason for the difference in climate is the positioning of land around the poles. The North Pole consists of an ocean surrounded by land, while the South Pole is the opposite, a land mass surrounded by ocean. Although this detail may seem meaningless, it actually has a drastic effect on the temperature of the poles.
The Southern Ocean is the only place where there is a ring of ocean, unbroken by land, surrounding the earth. This causes ocean currents to circle Antarctica in what is known as the Circumpolar Current. This current is one of the strongest in the world, and causes massive waves in the Southern Ocean. These waves make countries like South Africa and New Zealand ideal for surfing, but make reaching Antarctica a difficult ordeal. The Circumpolar Current also insulates the continent from warmer air farther north, making it much colder than the Arctic.
[read more]
The Sugar River, also known as The Upper Sugar River Watershed, is located in Dane County and flows all the way down to the Rock River.
[read more...]
It is getting easier to see black bears in Wisconsin. It’s becoming more common to see black bears because their numbers in Wisconsin are growing. So, if you decide to go camping in our state, it's possible you could see a black bear roaming around.
[read more...]
Did you know that when cows burp or fart they release a gas called methane that is toxic for our atmosphere? When scientists added seaweed in small amounts to the diet of a group of cows, the cows showed a reduction in the release of methane.
[read more...]
Imagine a future where storms, droughts, and floods are much more destructive and much more common than they are today. In this foreseeable future, the world's ecosystems have altered completely with polar bears and many other animals extinct and others migrating across the globe. Diseases exist in areas they had never been before. This future could become a reality if humans do not slow down the current global warming problem.
[read more...]
Although one might think the Arctic and Antarctic seem basically the same climate wise, they are actually noticeably different. Likewise, they are also affected differently by climate change. Both areas have melting ice, however the two poles have it for a different reason.
[read more...]
Over the last two decades, food that consumers have eaten contains genes from other plants that make them either grow faster, taste better or stay fresher for a longer period of time. Foods that have been altered this way are called “genetically modified foods.”
[read more...]
Native bee populations are declining. They are being threatened by urbanization and new farming techniques which can both poison the bees and harm their food source. Yet, there are ways that communities and individuals can help the bees.
[read more...]
The lesser long-nosed bat is no longer endangered thanks to conservation made possible by scientists and volunteers. It is the first U.S. bat to escape endangerment. The bats' recovery is thanks to cooperation between the United States and Mexico.
[read more...]
Recent developments have uncovered huge termite mounds completely covering a vast area in northeastern Brazil, previously covered by thick forests. These masses of earth can be up to three meters tall, and up to ten meters wide. They cover an area roughly the size of England. The combined mass of all the mounds can be seen from low earth orbit, though it is difficult to see individual mounds from that height.
[read more...]
California has experienced many wildfires in the past, but few, if any, have been as deadly as the recent Camp Fire. The future regarding this disastrous event is uncertain. The devastating wildfire burned for over two weeks, killed more than 85 people, and burdened thousands of lives. It will be remembered for many years to come.
[read more...]
European settlers such as Frank Hudson gave the Yahara Lakes beautiful Native American names. Lake Monona, Lake Mendota, Lake Kegonsa among other lakes are well-known to Madison residents; but many do not know why the settlers chose such a specific style of names.
[read more...]
Native plants are an important part of our ecosystem due to their many benefits, but their numbers are quickly dwindling. A new program by the Land and Water Resources Department aims to encourage more native gardens around Dane County. The program, called Plant Dane, is growing and offering free native plants to schools and community centers. Native plant gardens can be quite costly due to the high price of native plants. By offering free plants from the county, schools and communities that previously didn't have the money to create a garden now can.
[read more...]
The majority of woolly mammoths went extinct 10,600 years ago when climate change caused their supply of drinking water to dry up. Scientists analyzed climate change and came to the conclusion that global warming likely led to the shallow waters responsible for the animal's demise.
[read more...]
Wetlands are a major factor in Wisconsin's ecology; however, we are treating our environment so badly that we are causing wetland loss at alarming rates. It has taken the state thousands of years to form approximately ten million acres of wetlands, but it has taken less than 200 years for humans to ruin these vital landforms.
[read more...]
What are snakeheads? A snakehead is an invasive fish with a cylindrical shape and sharp teeth. An invasive species is a non-native organism that can harm an ecosystem. Snakeheads are separated into two genera: parachanna and channa. They are native to various parts of Africa and Asia; however, in 2002, the northern snakehead was caught in a Maryland pond. This immediately gained national attention and indicated that snakeheads were reproducing around the Maryland-Virginia area as well as in other states such as Wisconsin, Maine, Florida, as well as along the east and west coasts.
[read more...]
American Martens are one of Wisconsin's rarest endangered species. They are small in size and look very similar to fellow members of the weasel family. In fact, they often get confused with Fishers and Stone Martens who also live in Wisconsin. American Martens are slowly disappearing; this is a problem on the rise that needs to be addressed.
[read more...]
When we think of volcanoes we usually think of destruction, but did you know they can also construct new islands? In this article you can learn how islands are formed, how they can change, and how life arrives there.
[read more...]
A recent study confirms the speculations that the snows of Kilimanjaro located in Tanzania, Africa, may be gone by 2022. Lonnie Thompson, a glaciologist at Ohio State University in Columbus, says that the ice on Kilimanjaro is disappearing at a concerning rate.
[read more...]
The biggest survey yet of western lowland gorilla and chimpanzee populations brings good and bad news. There are more of the animals than previously thought, but their numbers are dropping rapidly due to a variety of factors. Will these creatures, which are so similar to us, be here in the generations to come?
[read more...]
A group of homeowners, businesses, and lake users, called the Friends of Lake Kegonsa, are going helping to implement a carp removal project. The project aims to remove a large number of these fish from Lake Kegonsa. For the past year, the staff at the Department of Natural Resources (DNR) in Wisconsin have been following a cluster of 20 carp that were captured, tagged, and set free last fall. They hope that if they follow the carp they will discover the migratory patterns of this invasive species.
[read more...]
According to a recent press release, Clean Wisconsin, a nonprofit organization that advocates for clean air and water, and the Wisconsin Farm Bureau released a statement addressing the recent policy updates to Natural Resources 151 (chapter 151 in the Wisconsin State Legislature). These updates are aimed at protecting the drinking water in Northeast Wisconsin and were implemented by the Department of Natural Resources.
[read more...]
Oceans hold many hidden mysteries of our planet. Deep among this waters are rich ecosystems that often go unnoticed and underappreciated by humans.
[read more...]
For some, Jamaican coffee is a staple. Whether it helps you wake up at the crack of dawn or it complements your afternoon doughnut, the world seems to run on coffee. Unfortunately, Jamaican coffee has been in decline for years. But there just might be hope for Jamaican coffee farmers and lovers, in the surprising form of birds.
[read more...]
There are five main oceans, and each one is special in its own way.
[read more...]
Some people view wolves as vicious predators but, in reality, their hunting habits actually help preserve nature's order.
[read more...]
Toshiba began to develop electronic technology in the 80's and 90's. Recently, the technology company has expanded its reach to include agriculture. In their indoor grow rooms, called “clean rooms,” Toshiba grows lettuce, spinach, and sprouts.
[read more...]
For some, Jamaican coffee is a staple. Whether it helps you wake up at the crack of dawn or it complements your afternoon doughnut, the world seems to run on coffee. Unfortunately, Jamaican coffee has been in decline for years. But there just might be hope for Jamaican coffee farmers and lovers, in the surprising form of birds.
[read more...]
At the University of Minnesota (UM) in Dakota County, agricultural researchers set up an eight- armed drone to send 200 feet in the air to begin its task. The drone is on the front line of their scientific explorations. Scientists at the UM are testing low-flying drones for their ability to find aphids, a grasshopper-like bug that ravages plants in the Upper Midwest.
[read more...]
Most people think that dust is just unnecessary molecules flying around. But as it turns out, dust is matter and it's important too.
[read more...]
Bees are important pollinators; however, they have recently been declining in population across the country. In response to this alarming trend, Ortho, a pesticide company and a and part of the Miracle-Grow family has decided to remove neonicotinoids or neonics, a chemical that may harm bees, from their home and garden products by 2021.
[read more...]
In East and Central Africa, many farmers and their families rely on the production of bananas. East Africa produces and consumes the most bananas in Africa. Unfortunately, a plant virus called Banana Xanthomonas Wilt (BXW) threatens to knock out production in this booming market. This alarms farmers because bananas are staple for them to provide food and income security.
[read more...]
Sea creatures provide food for most of the world's population. Luckily, the Earth's surface is 71 percent water and most of this water teams with aquatic life.
[read more...]
A reef is an area found at the bottom of an ocean where different kinds of colorful coral, fish, crab, starfish, and many other aquatic animals can be found.
[read more...]
Last year, the United Nations proclaimed 2015 as the International Year of Soils. A whole year dedicated to dirt? Though it may seem simple, dirt is more important than many people might think.
[read more...]
You might know algae as the little green particles that float atop lakes. But did you know that algae is a source of biofuel that can produce four types of oil.
[read more...]
Butterflies often grace the skies with their beautiful presence. But these winged-creatures haven’t always been so beautiful: they transition from caterpillars to become their final form.
[read more...]
Deep below the ocean surface where sunlight cannot reach, organisms have adapted in astounding ways to deal with total darkness.
[read more...]
Many types of sea life are disappearing due to changes in the underwater ecosystem. Overfishing and global warming are the roots of this problem. Because of this, you might think all aquatic species would be in danger. But, dive deeper into the ocean and you’d see a surprising survivor –– the jellyfish.
[read more...]
You know what they say, the stirrings of a butterfly's wings might cause a hurricane. However, butterflies’ wings have been stirring a lot less lately.
[read more...]
Animals living in the freezing Arctic have adapted in several ways to survive. Seals survive the frigid water because of their thick skin, for example. In contrast, sea lions can stay out of the water because they have back flippers to push themselves around on land.
[read more...]
Spring has finally sprung. Hello flowers, bees, and honey! But how is honey made?
Honey is a very versatile food. People use it to sweeten drinks and foods, eat it plain, or put it on food as a topping. However, there is a long process before this sweet goo ends up on your plate.
[read more...]
Mining involves digging into the earth to find useful, valuable substances. The second of humankind’s earliest endeavors (after agriculture), the practice of mining for coal, gas, salt, mineral ores, gemstones, and building materials has existed for centuries.
[read more...]
Many people do not realize how valuable water is until it's gone. Worldwide, droughts affect over 1.5 billion people in the developing world. California, one place currently affected by severe droughts, is working on a project that will improve water supply and hopefully get rid of some of its recently mandated water laws.
[read more...]
Every year thousands of helpless animals are illegally hunted, bringing them one step closer to extinction by poachers. But with new technology, these crimes can be stopped. The animal's potential savior—drones.
[read more...]
Do you remember Crush the sea turtle from the movie Finding Nemo? He took long, awesome journeys across the ocean. So do many green turtles. Green turtles are very interesting; from their horny plates that serve as teeth, to the 1,600 eggs they lay every year, there is much to learn about these unique creatures.
[read more...]
Some scientists are predicting that a lack of solar activity in 2030 could cause a mini ice age, which hasn't occurred in over 300 years!
[read more...]
Wind farms are a great source of energy. In the past, however, they have had a complicated relationship with wildlife. Yet, wind farms among British and German waters have recently been beneficial for marine creatures like harbor seals
[read more...]
Nuclear energy, produced by the combination of protons and neutrons inside atomic nuclei, is the energy that allows stars to shine so brightly. Two kinds of reactions release this energy: fission and fusion.
[read more...]
Wisconsin is ready to handle U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's upcoming pollution standards according to two environmental groups. In fact, Wisconsin has been doing so well that the state’s proposed carbon dioxide levels for 2030 are 30 percent below what they were in 2005.
[read more...]
The Triassic world emerged after the end-Permian mass extinction which almost wiped out life on earth. During the Triassic era, the world's reptiles first appeared.
[read more...]
ave you heard of Noturus gyrinus? What about Pylodictis olivaris? Or Ictalurcs punctacus? Maybe you have heard of the catfish? The name “catfish” comes from its cat-like whiskers. These whiskers, or barbels, are organs around the mouth that are used for touch, taste, and to find food.
[read more...]
When people think of birds in the rainforests they might initially picture a toucan. These unique animals have become a symbol of tropical America.
[read more...]
Over the past three decades, zebra mussels have found their way into United States’ waters. Native to the Black and Caspian seas, these mussels travel by latching onto sea-going ships or stowing away in ships’ ballasts. Now, zebra mussels can be found in the Mississippi River, some parts of California, and even the Great Lakes.
[read more...]
Recently estimated at fewer than 10,000, the mink population may be in deep water. In fact, the semi-aquatic creatures are losing their habitats at a rapid rate.
[read more...]
For the past 12,000 years, the American Pika, a small rabbit-like animal, has been retreating farther and farther up their home in the mountains. In fact, in the last century one third of their population in Oregon and Nevada has completely ceased to exist.
[read more...]
Gray whales can grow as large as a bus. On average, gray whales are 40 to 50 feet long and are typically covered by small parasites. Unlike most ocean creatures, gray whales are mammals. They are also omnivores, which means that they eat both plants and smaller sea creatures.
[read more...]
High foreclosure rates have resulted in abandoned homes which are becoming habitats for unpleasant occupants no one wants living next door—mosquitoes.
[read more...]
Humans have always impacted the environment. Since the 1800s, however, global industrialization, urbanization, and increases in population have had unforeseen consequences for the Earth.
[read more...]
Student activists at more than 200 colleges are looking for new ways to slow down climate change. In an effort to do so, these students are asking their colleges to stop investing money in fossil fuel companies.
[read more...]
Contrary to what one might think, coral reefs are home to many sea creatures.
[read more...]
Believe it or not, cows contribute to global warming more than you might think. A single cow can release about 18 cubic feet of methane gas everyday.
[read more...]
Medications that people use are starting to appear in rivers and streams all over the world. These drugs are negatively affecting the fish living in those waters.
[read more...]
|
|

